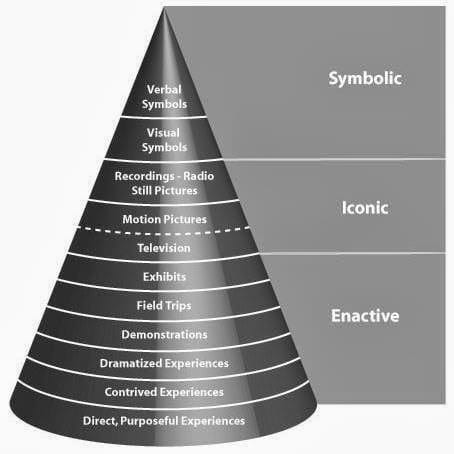
A Historical Perspective on Educational Innovation
Throughout history, the classroom has been a crucible of innovation, constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of society. From the introduction of the humble chalkboard in the early 19th century to the rise of artificial intelligence in the 21st, each technological advancement has promised to revolutionize the way we teach and learn. Today, we stand on the cusp of another transformation with the advent of text-based and multimodal AI. To understand its potential impact, we must first look back at the path that has led us here.
The March of Progress: Key Innovations in Education
- The Chalkboard (Early 19th Century): The chalkboard, introduced in the 1800s, marked a significant shift from individual slates to a shared visual learning space. This simple tool enhanced group instruction and allowed for dynamic, erasable content creation.
- The Ballpoint Pen (1940s): The mass production of ballpoint pens in the 1940s democratized writing, making it more accessible and efficient for students to take notes and complete assignments.
- Educational Television (1950s-1960s): Programs like “Sesame Street” brought visual and auditory learning into homes and classrooms, expanding the reach of education beyond traditional boundaries.
- Personal Computers (1980s-1990s): The introduction of personal computers in schools opened new avenues for interactive learning, word processing, and access to digital information.
- The Internet (1990s-2000s): The World Wide Web transformed research and collaboration, providing students and educators with unprecedented access to global knowledge.
- Learning Management Systems (2000s): Platforms like Blackboard and Moodle centralized course materials, assignments, and communication, facilitating both in-person and distance learning.
- Mobile Devices and Apps (2010s): Smartphones and tablets, along with educational apps, made learning more portable and personalized than ever before.
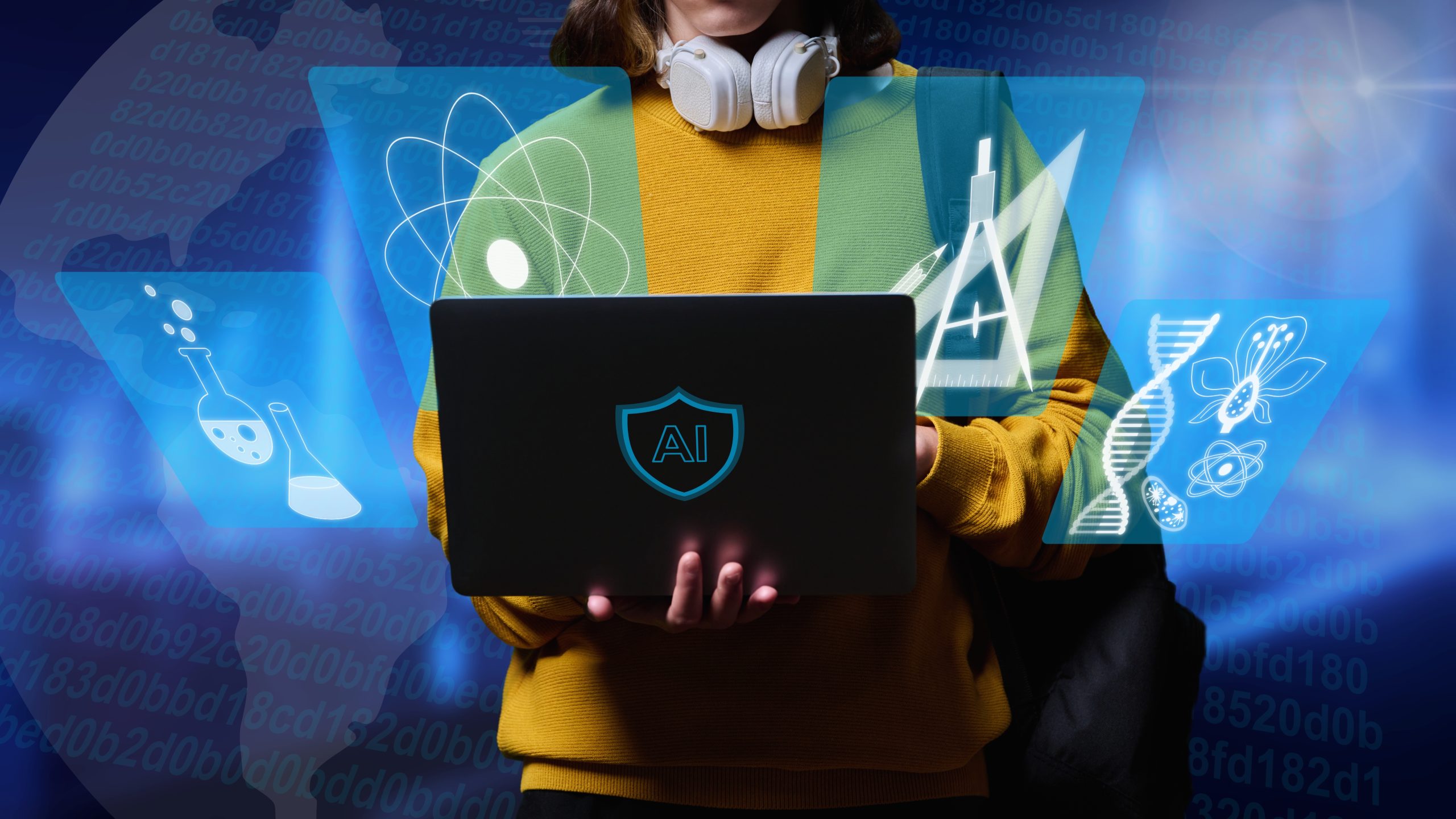
The AI Revolution: A New Frontier in Education
Now, as we enter the 2020s, artificial intelligence stands poised to redefine education once again. Like its predecessors, AI promises to enhance critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. However, it also brings unique capabilities that set it apart from previous innovations.
Text-Based Generative AI
Tools like ChatGPT represent a leap forward in interactive learning. Unlike static textbooks or one-way video lectures, these AI systems can engage in dynamic dialogue, answering questions, generating content, and adapting to individual student needs in real-time.
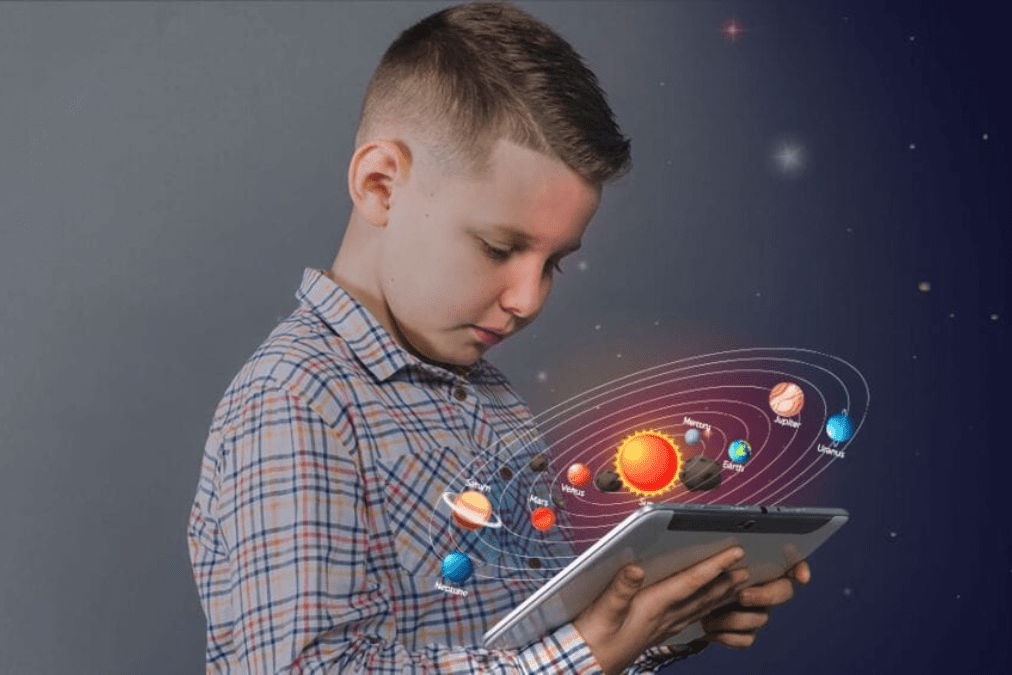
Multimodal AI: Beyond Text
While text-based AI is groundbreaking, multimodal AI takes the potential even further. These systems can process and generate not just text, but also images, audio, and even video. This multisensory approach mirrors the diverse ways humans learn and communicate, offering:
- Visual learners can benefit from AI-generated diagrams, infographics, and art.
- Auditory learners can interact with AI through voice commands and receive spoken explanations.
- Kinesthetic learners might soon interact with AI through augmented or virtual reality interfaces.
Comparative Advantages of AI in Education
Like the chalkboard expanded group learning, AI expands personalized learning to unprecedented scales. Similar to how educational innovation television brought expert presenters into the classroom, AI brings the collective knowledge of the internet to each student’s fingertips, but with the added ability to interact and ask questions.
However, AI goes beyond these past innovations in several ways:
- Adaptability: Unlike static tools, AI can adjust its teaching style and content based on individual student responses and progress.
- Scalability: While human tutors are limited in the number of students they can assist, AI can potentially provide one-on-one support to millions simultaneously.
- Continuous Improvement: As AI systems learn from interactions, they have the potential to improve over time, much like how the internet continually expands its knowledge base.
- Multimodal Integration: By combining text, image, audio, and potentially tactile interfaces, multimodal AI can cater to diverse learning styles more effectively than any single previous technology.
Challenges and Considerations
As with all educational innovations, the integration of AI into classrooms comes with challenges. Privacy concerns, the potential for misinformation, and the need for digital literacy were not issues faced by educators introducing chalkboards or ballpoint pens. Moreover, the rapid pace of AI development may require more frequent adaptations of curriculum and teaching methods than previous technologies demanded.
Embracing the Future While Learning from the Past
As we stand at this technological crossroads, it’s crucial to approach AI in education with both enthusiasm and caution. By understanding the historical context of educational innovation, we can better anticipate the potential impacts and challenges of AI integration.
The story of education is one of constant evolution, with each new tool building upon the foundations laid by its predecessors. Text-based and multimodal AI represent the next chapter in this ongoing narrative, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills for learners around the globe.
As educators and students alike navigate this new frontier, they do so standing on the shoulders of centuries of innovation, armed with the wisdom of past transitions and the promise of future potential. In this light, AI is not just a new tool, but a continuation of humanity’s enduring quest to expand the boundaries of knowledge and learning.
Check out our newsletters !












-1024x826.jpg)